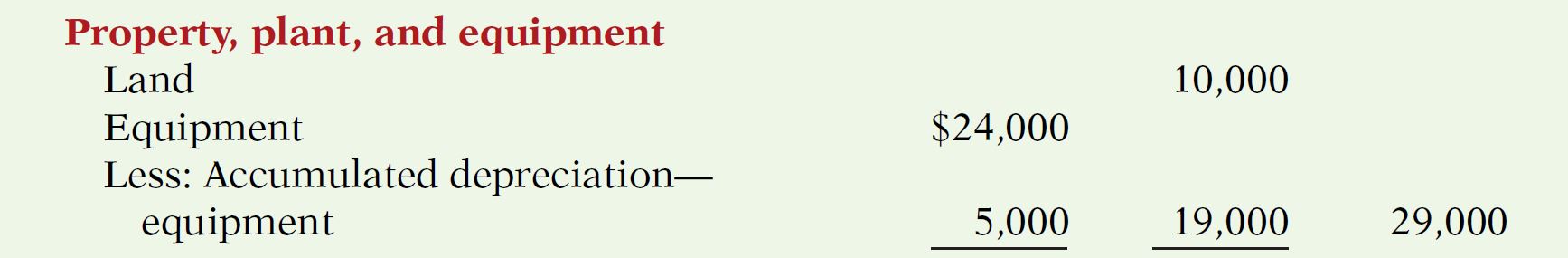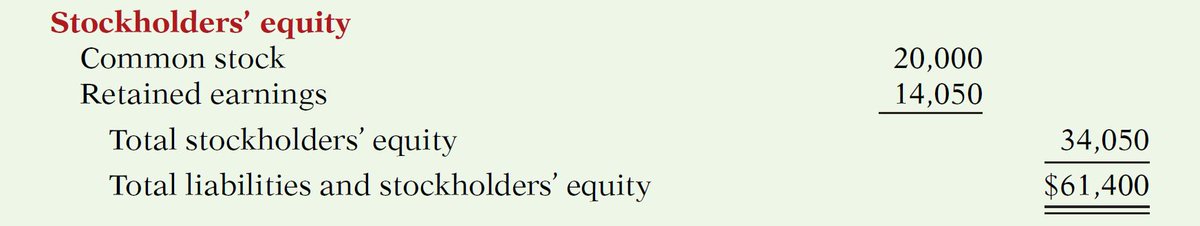Thread by Kenny | Accent Investing
- Tweet
- May 17, 2023
- #Personalfinance
Thread
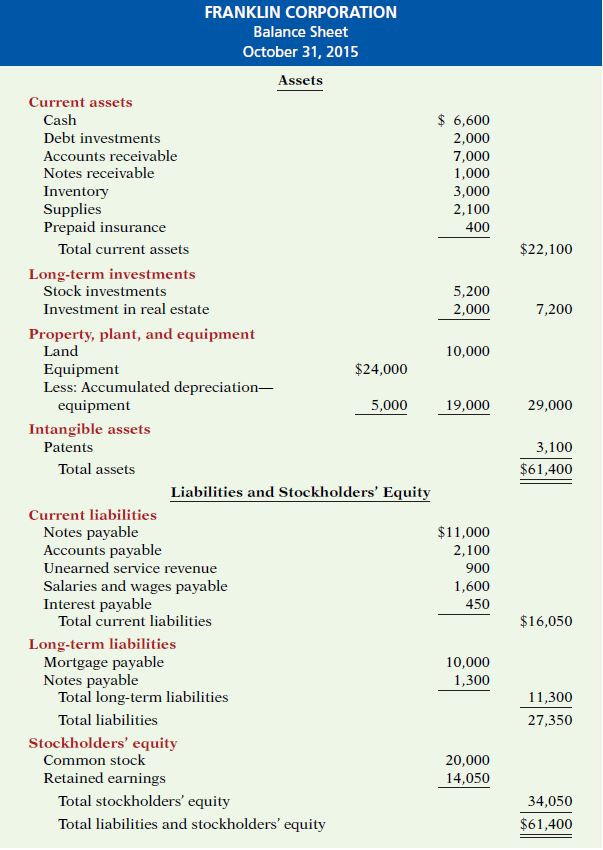
A balance sheet is a snapshot of a business at a specific point in time. It serves two purposes.
Internally, it provides information about the financial health of a company.
Externally, it depicts the business's resources and how they are financed.
Internally, it provides information about the financial health of a company.
Externally, it depicts the business's resources and how they are financed.
It shows the company's assets, liabilities, and shareholders' equity.
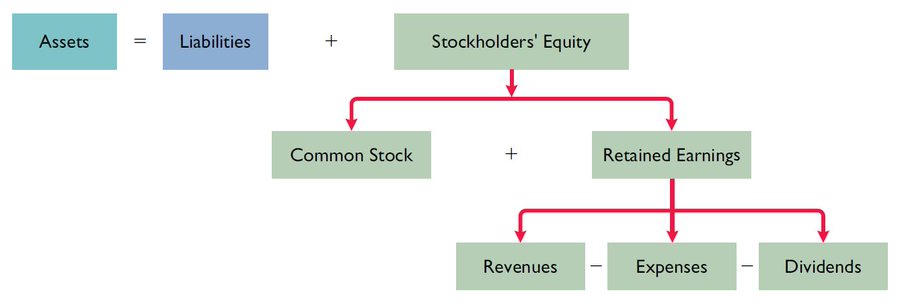
The equation to remember is: ASSETS = LIABILITIES + EQUITY
The equation to remember is: ASSETS = LIABILITIES + EQUITY
• ASSETS
Assets are what a company owns.
Current assets are assets that a company expects to convert to cash within a year.
They include:
• Cash
• Investments
• Receivables
• Inventories
•Prepaid expenses
They help in determining short-term debt-paying ability.
Assets are what a company owns.
Current assets are assets that a company expects to convert to cash within a year.
They include:
• Cash
• Investments
• Receivables
• Inventories
•Prepaid expenses
They help in determining short-term debt-paying ability.
Non-current assets are long-term investments that are unlikely to be converted into cash in the near future, such as:
Non-current assets include:
• Investments in stocks and bonds
• Lands or buildings
• Long-term notes receivable
Non-current assets include:
• Investments in stocks and bonds
• Lands or buildings
• Long-term notes receivable
Property, plant, and equipment
They are assets with relatively long useful lives that a company is currently using in operating the business.
This category includes:
• Land,
•Buildings,
•Machinery and equipment
• Delivery equipment and furniture.
They are assets with relatively long useful lives that a company is currently using in operating the business.
This category includes:
• Land,
•Buildings,
•Machinery and equipment
• Delivery equipment and furniture.
Depreciation is the practice of allocating the cost of assets over a number of years.
The accumulated depreciation account shows the total amount of depreciation that the company has expensed thus far in the asset’s life.
The accumulated depreciation account shows the total amount of depreciation that the company has expensed thus far in the asset’s life.
Intangible Assets
They are long-term assets that lack physical substance but are frequently very valuable.
Other intangible assets include:
• Goodwill
• Intellectual property
• Brands
• Trademarks
They are long-term assets that lack physical substance but are frequently very valuable.
Other intangible assets include:
• Goodwill
• Intellectual property
• Brands
• Trademarks
• LIABILITIES
Liabilities are what a company owes.
Current liabilities are obligations that the company must pay within the next year or cycle of operations.
They include:
• Accounts payable
• Wages payable
• Notes payable
• Interest payable
• Income taxes payable
Liabilities are what a company owes.
Current liabilities are obligations that the company must pay within the next year or cycle of operations.
They include:
• Accounts payable
• Wages payable
• Notes payable
• Interest payable
• Income taxes payable
The relationship between current assets and current liabilities helps evaluate the liquidity of a company.
When current assets are higher than current liabilities, the company is in a good position to pay its short-term creditors.
If not, the company can go bankrupt.
When current assets are higher than current liabilities, the company is in a good position to pay its short-term creditors.
If not, the company can go bankrupt.
Long-term liabilities are obligations that a company expects to pay after one year.
Long-term liabilities include:
• Bonds payable
• Mortgages payable
• Long-term notes payable
• Lease liabilities
• Pension liabilities
Long-term liabilities include:
• Bonds payable
• Mortgages payable
• Long-term notes payable
• Lease liabilities
• Pension liabilities
• STOCKHOLDER’s (OWNERS') EQUITY
This is the ownership claim on the company's assets.
This section of the balance sheet consists of common stock and retained earnings.
If you add all the resources of a company and subtract its liabilities, what is left is the equity.
This is the ownership claim on the company's assets.
This section of the balance sheet consists of common stock and retained earnings.
If you add all the resources of a company and subtract its liabilities, what is left is the equity.
• HOW TO ANALYZE A BALANCE SHEET
We can analyze it using ratios.
Financial ratios are generally divided into four categories:
• Liquidity
• Solvency
• Efficiency
• Profitability
With the balance sheet, we will focus on the first three ratios
We can analyze it using ratios.
Financial ratios are generally divided into four categories:
• Liquidity
• Solvency
• Efficiency
• Profitability
With the balance sheet, we will focus on the first three ratios
• Liquidity Ratios
Measure the short-term debt-paying ability of a company.
• Current Ratio =Current Assets / Current Liabilities
• Quick Ratio =Cash & Cash Equivalents + Accounts Receivables) / Current Liabilities
• Cash Ratio =Cash & Cash Equivalents / Current Liabilities
Measure the short-term debt-paying ability of a company.
• Current Ratio =Current Assets / Current Liabilities
• Quick Ratio =Cash & Cash Equivalents + Accounts Receivables) / Current Liabilities
• Cash Ratio =Cash & Cash Equivalents / Current Liabilities
A ratio between 1-3 is a good sign for a company, suggesting that a business has enough cash to be able to pay its debts.
A ratio of less than 1 means that the company can't pay its debts. It may be necessary to finance or extend the time required to pay creditors.
A ratio of less than 1 means that the company can't pay its debts. It may be necessary to finance or extend the time required to pay creditors.
• Solvency Ratios
Measure a company's long-term paying ability.
• Debt-To-Equity Ratio = Total Debt / Total Equity
• Debt Ratio = Total Debt / Total Assets
The higher the ratio, the more debt and risk the company has.
Measure a company's long-term paying ability.
• Debt-To-Equity Ratio = Total Debt / Total Equity
• Debt Ratio = Total Debt / Total Assets
The higher the ratio, the more debt and risk the company has.
• Efficiency Ratios
Measure the efficiency of converting assets into cash.
• Receivables Turnover Ratio =Sales / Accounts Receivable
• Inventory Turnover Ratio =COGS / Inventories
• Asset Turnover Ratio =Sales / Total Assets
Efficiency ratios can also be measured in days.
Measure the efficiency of converting assets into cash.
• Receivables Turnover Ratio =Sales / Accounts Receivable
• Inventory Turnover Ratio =COGS / Inventories
• Asset Turnover Ratio =Sales / Total Assets
Efficiency ratios can also be measured in days.
If you enjoyed this thread, please like, comment, and retweet the first tweet.
I write about
• Personal Finance
• Investing
• Wealth
Follow me @AccentInvesting for more tips.
Subscribe to receive a free guide on the top 5 ETFs to hold for life: bit.ly/AccentInvesting
I write about
• Personal Finance
• Investing
• Wealth
Follow me @AccentInvesting for more tips.
Subscribe to receive a free guide on the top 5 ETFs to hold for life: bit.ly/AccentInvesting