Thread by Kenny | Accent Investing
- Tweet
- May 16, 2023
- #Personalfinance
Thread
An income statement is a summary of the total impact of revenue, expense, gain, and loss transactions for a given period.
It is also referred to as:
• Statement of operations
• Statement of earnings
• Profit and loss (P&L) statement
It shows how profitable a business is.
It is also referred to as:
• Statement of operations
• Statement of earnings
• Profit and loss (P&L) statement
It shows how profitable a business is.
• The content of an income statement
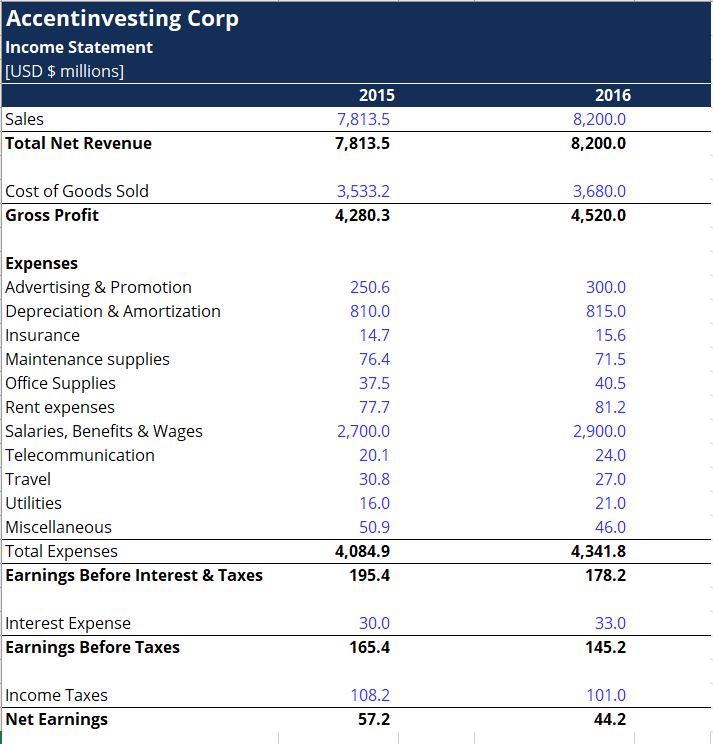
The income statement contains important information about how a company earns its money and how it spends it.
An income statement includes the following categories:
The income statement contains important information about how a company earns its money and how it spends it.
An income statement includes the following categories:
• Revenue/ Sales
Revenues are money a business makes in during a reporting period.
Typical revenues include:
• Net sales: from a business producing or selling products.
• Service revenues: from a business providing services.
Revenues are money a business makes in during a reporting period.
Typical revenues include:
• Net sales: from a business producing or selling products.
• Service revenues: from a business providing services.
• Expenses
Expenses are money a business spends during a reporting period.
• Cost of Goods sold
This line item includes direct costs associated with the sale of products to generate income.
In companies whose main revenue is service, it is also known as cost of sales.
Expenses are money a business spends during a reporting period.
• Cost of Goods sold
This line item includes direct costs associated with the sale of products to generate income.
In companies whose main revenue is service, it is also known as cost of sales.
• Gross Profit
Gross profit is calculated by deducting the cost of goods sold (or cost of sales) from the sales revenue.
Gross profit is calculated by deducting the cost of goods sold (or cost of sales) from the sales revenue.
• Marketing, Advertising, and Promotion Expenses
These are expenses that relate to the promotion and advertising to generate revenue for the business.
These are expenses that relate to the promotion and advertising to generate revenue for the business.
• Selling, general and administrative (SG&A) expenses
These are all other indirect costs associated with running the business.
They include:
•Salaries and wages
•Rent and office expenses
•Insurance
•Travel expenses
All the expenses above are named operating expenses.
These are all other indirect costs associated with running the business.
They include:
•Salaries and wages
•Rent and office expenses
•Insurance
•Travel expenses
All the expenses above are named operating expenses.
• Operating income: Gross profit - operating expenses
• EBITDA (Earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization) It is calculated by subtracting SG&A expenses (excluding amortization and depreciation) from gross profit.
• EBITDA (Earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization) It is calculated by subtracting SG&A expenses (excluding amortization and depreciation) from gross profit.
• Depreciation & Amortization Expense: non-cash expenses to spread out the cost of capital assets such as Property, Plant, and Equipment.
• EBIT (Earnings Before Interest and Taxes): profit before any non-operating income, expenses, interest, or taxes are reduced from revenue.
• EBIT (Earnings Before Interest and Taxes): profit before any non-operating income, expenses, interest, or taxes are reduced from revenue.
• Interest expense: this can be either an expense or an income. This is useful to distinguish EBIT from EBT.
• EBT (Earnings Before Tax): it is calculated by subtracting interest expense from operating income.
• EBT (Earnings Before Tax): it is calculated by subtracting interest expense from operating income.
• Income taxes are the applicable taxes charged to the business for performing its activities.
• Net income: earnings remaining after subtracting the income tax expense. This is the amount that goes into retained earnings on the balance sheet after any dividends are deducted.
• Net income: earnings remaining after subtracting the income tax expense. This is the amount that goes into retained earnings on the balance sheet after any dividends are deducted.
• How to analyze an income statement
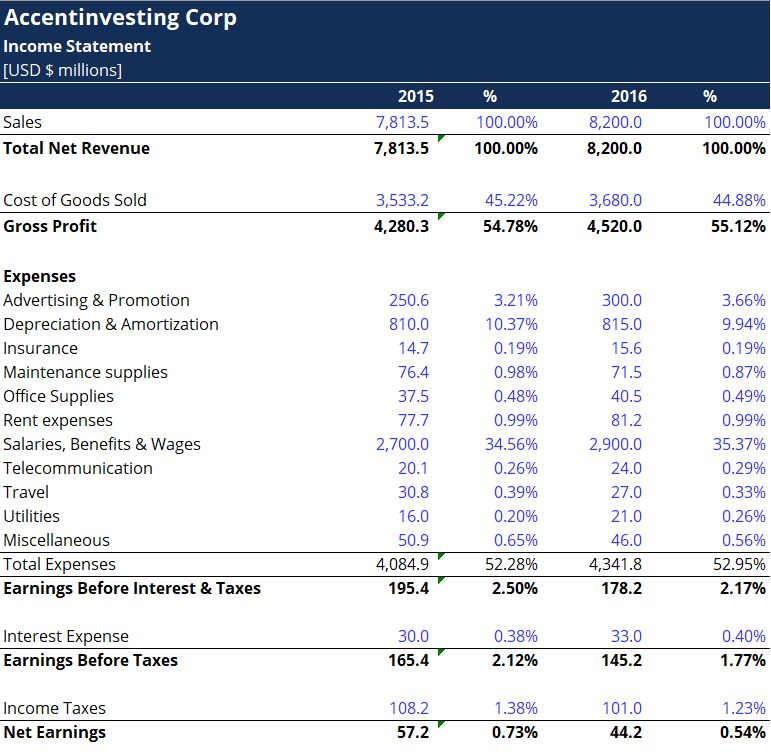
• Vertical Analysis
It is a method of financial analysis where each line item is listed as a percentage of a base figure within the statement.
It is especially convenient to perform the analysis on a comparative basis.
• Vertical Analysis
It is a method of financial analysis where each line item is listed as a percentage of a base figure within the statement.
It is especially convenient to perform the analysis on a comparative basis.
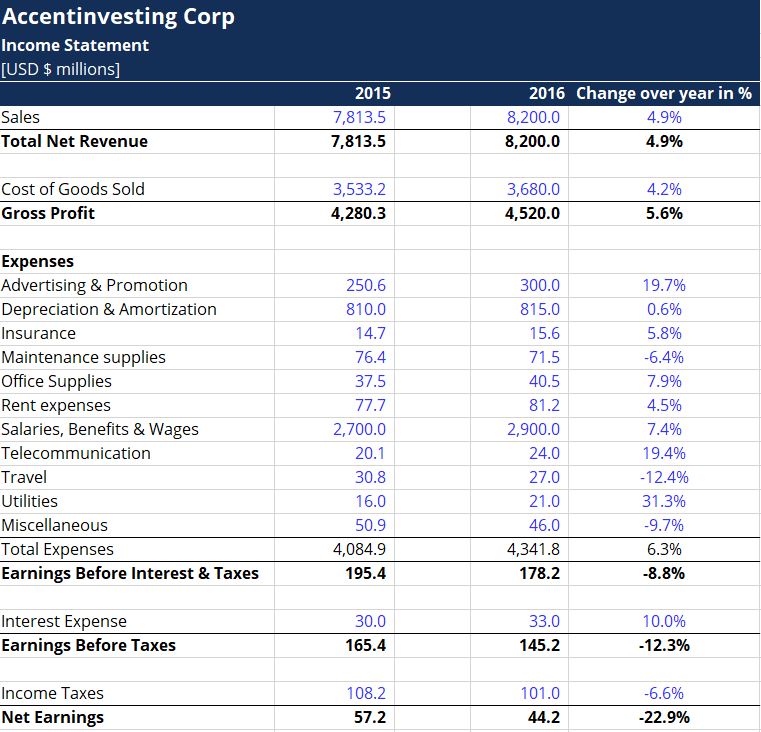
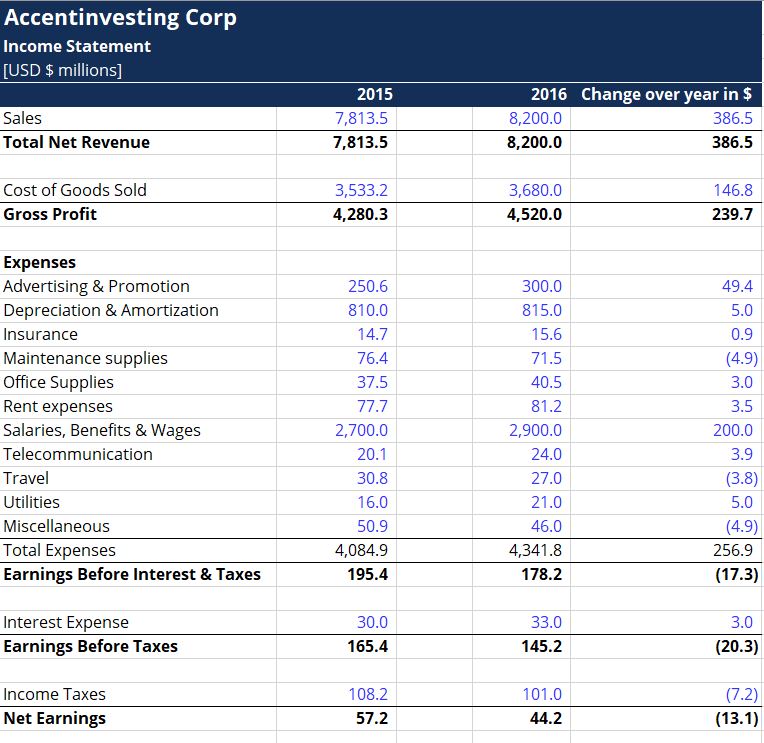
• Horizontal Analysis
It compares changes in the dollar amounts in a company’s financial statements over multiple reporting periods.
This can be expressed in absolute amount or in percentage.
Its purpose is to determine the increase or decrease that has taken place.
It compares changes in the dollar amounts in a company’s financial statements over multiple reporting periods.
This can be expressed in absolute amount or in percentage.
Its purpose is to determine the increase or decrease that has taken place.
• Ratio Analysis
It shows various pieces of financial information in the financial statements of a business.
• Gross profit margin: shows a company's earnings after deducting the costs of producing its goods and services.
Gross profit margin: Gross profit / Revenue or Sales.
It shows various pieces of financial information in the financial statements of a business.
• Gross profit margin: shows a company's earnings after deducting the costs of producing its goods and services.
Gross profit margin: Gross profit / Revenue or Sales.
• The profit margin measures the net income generated by each dollar of sales.
Profit Margin: Net income/ Revenue or sales
Profit Margin: Net income/ Revenue or sales
• Operating profit margin is a profitability or performance ratio that reflects the percentage of profit a company produces from its operations before subtracting taxes and interest charges.
Operating profit margin = Operating income/ Revenue or sales.
Operating profit margin = Operating income/ Revenue or sales.
• Return on Assets: It reveals the after-tax profit a company generates for every dollar of assets it holds.
ROA = Net income/ Assets
• Return on equity: It measures the rate of return on the money that equity investors have put into the business.
ROE = Net income/ Equity
ROA = Net income/ Assets
• Return on equity: It measures the rate of return on the money that equity investors have put into the business.
ROE = Net income/ Equity
• The debt service coverage ratio is the percentage of operating income available for debt servicing (interest and principal payments).
DCR = Operating Income / Debt service
A lot of lenders will look at this ratio to decide whether they will lend you money.
DCR = Operating Income / Debt service
A lot of lenders will look at this ratio to decide whether they will lend you money.
If you enjoyed this thread, please like, comment, and retweet the first tweet.
I write about
- Personal Finance
- Investing
- Wealth
Follow me @AccentInvesting for more tips.
Subscribe to receive a free guide on the top 5 ETFs to hold for life: bit.ly/AccentInvesting
I write about
- Personal Finance
- Investing
- Wealth
Follow me @AccentInvesting for more tips.
Subscribe to receive a free guide on the top 5 ETFs to hold for life: bit.ly/AccentInvesting
Mentions
See All
Growth Hub @growthhub_
·
May 16, 2023
Fantastic thread 🔥🔥